How to Rank on Page 1 of Google
Wondering how to rank on page one of Google ?
The truth is it’s getting harder and harder for local businesses to accomplish. As Google’s algorithm continues to evolve, the quick techniques that worked five years ago no longer have the same effect.
Instead, ranking on page one now requires optimizing numerous critical factors. Cumulatively, these factors work together to tell Google your website is relevant, authoritative, and worth ranking high.
So, is it even worth the trouble? YES! Ranking on page one is definitely more difficult than it used to be, but the effects are the same: more traffic from organic search and potentially a lot more business.
In this post, discover some key ways to improve your website’s SEO and jump higher in Google’s rankings—maybe even all the way to page one.
Note: These tips are geared toward local search and use local SEO techniques. Ranking at the national level can require different SEO strategies.
The Basics: How to Rank on Page 1 of Google
Every industry is different, but some SEO techniques work for virtually all industries. Here’s what we recommend for raising your rankings:
1. Optimize Your Website (Or Get a New One)
Your website can be the most powerful part of your online presence—or your weakest link. Here are the top factors that affect your website’s performance in search results:
- Is your website mobile-responsive?
- It your website secure?
- Does your website load quickly?
- Has your domain been around for more than a year?
- Does your website contain high-quality content?
- Does your website contain relevant keywords, and are they featured in places like your URL, title tags, meta-descriptions and headers?
- Do other websites (such as online directories) link to your website?
If you answered yes to the above questions, great! Your website is likely optimized for organic search. If not, you have some work to do.
All of the above factors play into how Google views your website—and consequently how high you rank. Taking time to change all of your “no” answers into “yes” can make a real difference in your search visibility.
Sometimes, that means you need to develop a brand new website , particularly if your current website is very outdated. Even the best SEO campaign won’t do much if your website’s overall quality is poor.
2. Choose the Right Keywords
“Keywords” are the words and phrases people type into Google to generate results. By optimizing your website for the keywords most relevant to your industry, you can often raise your search engine rankings. The best places to include your keywords are in your:
- URLs
- Title tags
- Meta-descriptions
- Headers
- Alt tags of images
Typically, it’s best to target one keyword per page of your website.
How do you determine which keywords to target? These days, going after the most searched keywords is typically ill advised. For example, pursuing “restaurant” is unlikely to help you rank higher for that term, because the restaurant industry is extremely competitive. In fact, unless you’re in a niche industry, the most searched keywords are almost always inaccessible these days.
Instead, you might want to pursue “Conshohocken restaurant” or “Thai restaurant” or even “Conshohocken restaurant with outdoor seating.” In other words, go after more specific keywords to improve your chances of ranking. Often, these keywords still receive significant search volume and can boost your traffic from organic search.
We offer a pay-for-performance SEO service in which we target strategic keywords—and we don’t charge our customers until they rank on page one. Learn more !
3. Complete Your Google My Business Profile
On par with your website, your Google My Business profile is essential for SEO.
Google My Business is the modern-day phonebook: perhaps the world’s largest online directory. Your Google My Business Listing appears in important places like Google’s Local Pack, Local Finder, Google Maps, and alongside organic rankings. All of these are central to your online visibility.
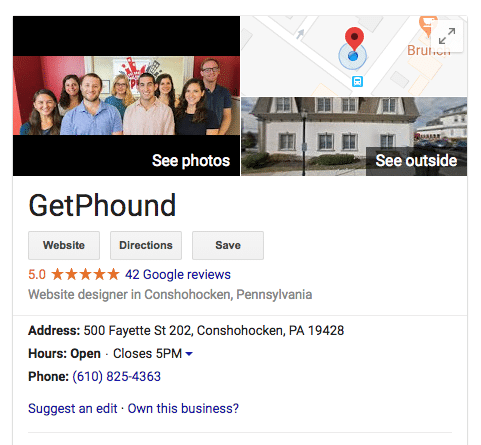
You can create your Google My Business profile easily , but be sure to verify it via phone or U.S. mail to gain complete control over it. As the owner of your listing, you can upload photos, broadcast events, update your hours and phone number, and accumulate and respond to reviews. Speaking of reviews…
4. Get As Many Reviews As You Can
Because so many potential customers are using tools like Google Maps and the Local Pack to discover businesses, it’s vital that you stand out in these results.
One way to accomplish this is by accumulating as many (positive) reviews as possible. A business with many positive reviews not only looks better than the competition; it has a greater likelihood of ranking higher!
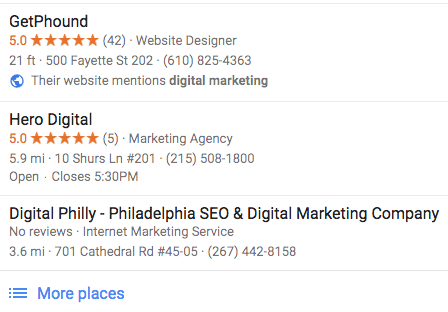
There are many ways to acquire reviews from happy customers, such as providing incentives like a free gift or discount. You might also want to establish a system for emailing recent customers for reviews. Need ideas for generating reviews? We can help.
5. Organic isn’t the Only Way
Last but not least, the fastest way to get to page one of Google is through “pay per click,” otherwise known as Google Ads.
Even if you’ve never heard of Google Ads, you’ve undoubtedly encountered it. Those first results at the top of Google are usually part of Google Ads, which is essentially a giant auction where bidders compete for clicks.
Sound expensive? For many businesses, the investment is worth it, since the ads attract highly qualified searchers who frequently turn into leads. Plus, for many businesses, the “cost per click” is less than you might think. Many of our customers pay less than $5 per click, and every click has the potential to turn into a customer.
Need Help Getting to Page One?
We specialize in helping businesses grow their online visibility. Make the most of your online presence! Contact us today for a free consultation to talk about how we can help your business grow.
The post How to Rank on Page 1 of Google appeared first on GetPhound.